
Consumer Insights
Uncover trends and behaviors shaping consumer choices today
Procurement Insights
Optimize your sourcing strategy with key market data
Industry Stats
Stay ahead with the latest trends and market analysis.
The Expert Market Research report, titled “Sulphur Coated urea (SCU) Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2026 Edition: Industry Trends, Capital Investment, Price Trends, Manufacturing Process, Raw Materials Requirement, Plant Setup, Operating Cost, and Revenue Statistics” includes various aspects that are critical for establishing a sulphur coated urea (SCU) plant. These include infrastructure requirements, transportation requirements, utility specifications, and financial and economic analysis, among others.
| Sulphur Coated Urea (SCU) Product Details: | |
| Product Name | Sulphur Coated Urea |
| Chemical Formula | CH4N2O (core urea) + S (sulphur coating) |
| Molar Mass | 60.06 g/mol (urea core) |
| Appearance and Color | Granular, yellow to off-white |
| CAS No. | 57-13-6 (urea) |
| Melting Point | 132–135°C (urea core) |
| Common Names | SCU, Controlled-Release Urea, Sulfur-Coated Fertilizer |
| Top Exporting Countries | USA, China, India, Brazil, Canada |
The demand for sulphur coated urea (SCU) is significantly driven by the increasing global population and the subsequent need for enhanced food production. As of 2024, the global population has reached approximately 8.2 billion and is projected to grow to around 10.3 billion by the mid-2080s, according to the United Nations. This surge in population creates an urgent need for higher agricultural yields to meet food demands. In India, which has become the most populous country with about 1.428 billion residents, surpassing China's 1.419 billion, the pressure on food production is particularly acute.
In response, India aims to increase its food grain production from around 300 million tons in 2024 to meet the nutritional needs of its growing population. SCU plays a crucial role in this context by providing a slow-release nitrogen source that enhances nutrient retention in soils, thereby supporting sustainable farming practices. Moreover, countries like Nigeria and Pakistan are also experiencing rapid population growth, with projections indicating that Nigeria's population could reach approximately 477 million by 2100. This demographic trend necessitates innovative agricultural solutions such as SCU to ensure food security in these regions.
Other elements to consider while establishing a sulphur coated urea (SCU) plant include raw material sourcing, workforce planning, and packaging. The production of sulphur coated urea (SCU) relies on several key raw materials, including urea, sulfur, and sealant components. Urea serves as the primary nitrogen source in SCU and is typically used in granulated form, which allows for effective coating with sulfur. Sulfur is another essential material, as it forms the protective coating that encapsulates the urea granules. During production, sulfur is heated to around 150°C and then sprayed onto preheated urea granules. Additionally, sealant components such as urea-formaldehyde resin and other additives like ammonium chloride and citric acid are used. These raw materials enable SCU to provide a controlled release of nitrogen, improving nutrient management in agricultural practices.
Moreover, to help stakeholders determine the economics of a sulphur coated urea (SCU) plant, project funding, capital investments, and operating expenses are analyzed. Projections for income and expenditure, along with a detailed breakdown of fixed and variable costs, direct and indirect expenses, and profit and loss analysis, enable stakeholders to comprehend the financial health and sustainability of a business. These projections serve as a strategic tool for evaluating future profitability, assessing cash flow needs, and identifying potential financial risks.
However, challenges such as environmental regulations, fluctuations in raw material prices, and the limited availability of suitable urea types may threaten supply stability. To combat this, manufacturers of sulphur coated urea (SCU) can invest in advanced production technologies, diversify their raw material sources, and collaborate with agricultural stakeholders to enhance education and awareness about the benefits of SCU. By adopting polymer coatings for better nutrient release and efficiency, manufacturers can improve product performance while addressing environmental concerns. Additionally, forming partnerships with farmers and agricultural organizations can facilitate the proper application of SCU. This proactive approach not only stabilises supply but also promotes the sustainable use of fertilisers in agriculture.
.webp)
Read more about this report - Request a Free Sample
Sulphur Coated Urea (SCU), also known as Urea Gold, is a slow-release fertiliser that enhances nitrogen use efficiency in crops. By coating urea granules with sulfur, SCU regulates nitrogen availability, promoting better plant growth. Typically containing 31%-38% nitrogen, it also supplies sulfur, essential for various metabolic processes in plants. SCU is particularly beneficial in rice and wheat cultivation, improving yields and reducing nitrogen leaching losses. SCU was developed at the Tennessee Valley Authority laboratories in the USA and has been commercially produced for nearly 30 years. In India, it has recently gained attention as a premium fertiliser alternative.
Sulphur Coated Urea (SCU) contains 31% to 38% nitrogen and about 17% sulfur, making it a dual-purpose fertiliser that not only provides essential nitrogen but also supplies sulfur, which is crucial for various metabolic processes in plants. The physical properties of SCU include a yellowish goldish colour, attributed to the sulfur coating, which acts as a semi-permeable barrier that controls the release of nitrogen. This coating allows for a gradual release of nitrogen over a period of 30 to 120 days, depending on environmental conditions, thereby significantly reducing nitrogen losses through leaching, volatilisation, and denitrification. The slow release improves nitrogen use efficiency by up to 30% compared to conventional urea, leading to better crop yields and reduced environmental impact. Additionally, SCU helps maintain soil health by minimising nitrogen runoff and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
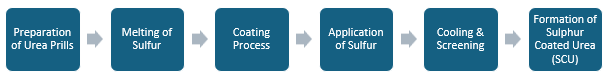
The production of sulphur coated urea (SCU) begins with the preparation of urea prills, where liquid urea is sprayed into a prilling tower to form small, round particles. Next, elemental sulfur is melted and heated to approximately 135°C (275°F). The urea prills are then transferred into a rotating drum, also heated to the same temperature, where the molten sulfur is sprayed onto the prills. This allows the sulfur to solidify and adhere to the urea. After coating, the prills are cooled and screened to eliminate any oversized or undersized particles before being bagged or stored for distribution.
Read more about this report - Request a Free Sample
SCU market growth is primarily driven by its ability to provide a slow and steady release of nitrogen and sulfur, promoting improved plant growth and yield. The growing demand for fruits and vegetables globally, along with the need to improve their quality and shelf-life, has led to increased adoption of SCU in the production of these crops. SCU is also gaining popularity in turf and ornamental applications, such as golf courses, sports fields, and residential lawns, due to its ease of use, cost-effectiveness, and ability to maintain healthy turfgrass. The rising preference for premium fertilisers, driven by the growing trend of landscaping in urban and residential complexes, is expected to further complement the growth of the SCU market.
A detailed overview of production cost analysis that evaluates the manufacturing process of sulphur coated urea (SCU) is crucial for stakeholders considering entry into this sector. Furthermore, stakeholders can make informed decisions based on the latest economic data, technological innovations, production process, requirements of raw materials, utility and operating costs, capital investments by major players, pricing strategies, and profit margins. For instance, the Indian government has recently initiated efforts to promote the production and sale of sulphur coated urea (SCU), branded as "Urea Gold," with a dual objective. Firstly, SCU aims to serve as a slow-release fertiliser that significantly enhances nitrogen uptake by crops, potentially increasing nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) by 10-15 percentage points.
Secondly, it addresses sulfur deficiencies in soils, particularly benefiting crops like oilseeds and pulses, which require more sulfur. SCU contains 37% nitrogen and 17% sulfur, providing a balanced nutrient profile compared to ordinary urea, which has 46% nitrogen.
Below are the sections that further detail the comprehensive scope of the prefeasibility report for a sulphur coated urea (SCU) production plant:
Market Dynamics and Trends: Growth factors such as the need for sustainable agricultural practices significantly affect market conditions in the sulphur coated urea (SCU) sector. The rising awareness regarding the negative impacts of conventional fertilisers, particularly their contribution to eutrophication and water pollution, has led to a greater demand for controlled-release fertilisers like SCU. Technological advancements in agriculture, such as precision farming techniques, are enhancing the effectiveness of SCU by improving nutrient application based on real-time data, thereby increasing its appeal among modern farmers. Understanding these trends helps businesses align their production plans with demands and trends in the sulphur coated urea (SCU) market.
Profiling of Key Industry Players: Leading manufacturers in the sulphur coated urea (SCU) market comprise a mix of global and Indian companies. Notable international players include Nutrien Ltd., J.R. Simplot Chemicals, Israel Chemicals Ltd., Syngenta AG, and Yara International ASA. In India, key contributors include Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilisers (RCF), Chambal Fertilisers and Chemicals Limited, Coromandel International Limited, and Gujarat State Fertilisers & Chemicals Ltd. As reported in December 2024, Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilisers (RCF) has achieved significant sales in the current year by selling 12,286 tons of sulphur coated urea, also known as Urea Gold. The commercial production of sulphur coated urea began at RCF's Trombay plant during the 2023-24 fiscal year. Since then, RCF has dispatched a total of 13,844 tonnes, indicating strong market demand across India.
Economic Analysis: Capital expenditure (CAPEX) analysis provides stakeholders the knowledge about required investments in advanced technologies, efficient machinery, and necessary infrastructure. Investing in high-capacity mixing equipment, such as a continuous mixer or high-shear mixer, can improve production efficiency by 20-30%. Investing in energy-efficient systems, such as combined heat and power (CHP) systems could reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, as these systems use waste heat from production processes to generate electricity and provide heating.
Fluctuations in sulphur coated urea (SCU) prices are significantly influenced by the costs of essential raw materials, particularly urea and sulphur. As of November 2024, the average price of urea is approximately USD 496 per ton, reflecting a decline of about 14% compared to the previous year. In June 2024, the Black Sea urea price reached USD 336 per ton, marking an 18% increase from May 2024, showcasing volatility in the market driven by supply and demand dynamics. Meanwhile, sulphur prices have also experienced fluctuations, contributing to overall production costs for SCU. In 2024, the price of SCU is projected to be approximately 12.5% higher than neem-coated urea.
Moreover, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) in India has approved the introduction of sulphur coated urea, priced at INR 266.50 for a 40 kg bag. This new fertiliser, branded as "Urea Gold," aims to enhance soil health, optimise nutrient release, and improve crop yields. The pricing strategy aligns with that of the 45 kg bags of Neem Coated Urea. This will benefit manufacturers by increasing demand for this eco-friendly fertiliser.
Establishing a sulphur coated urea (SCU) manufacturing facility requires a comprehensive financial investment that encompasses various elements critical to the project's success. The following sections detail these components:
Projected profit margins and effective product pricing strategies improve overall profitability. Manufacturers might target a profit margin of around 20-30%, achieved through strategic pricing based on raw material costs and prevailing market demand. Effective pricing strategies should consider fluctuations in raw material prices and competitive positioning within the market.
The establishment of a sulphur coated urea (SCU) manufacturing facility must comply with various regulatory frameworks that govern production standards.
Key regulations include the New Urea Policy (NUP-2015), which aims to maximise indigenous urea production while promoting energy efficiency and rationalising government subsidies. The Environmental Protection Act also plays a crucial role in regulating the environmental impact of fertiliser production. Additionally, the Fertiliser Control Order (FCO) mandates specific quality standards and labelling requirements for fertilisers, including SCU, to guarantee their safety and efficacy for agricultural use. Compliance with Manufacturing Standards set by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) is also essential, as these standards outline the technical specifications and quality assurance processes necessary for producing SCU. Furthermore, adherence to the Chemical Accidents (Emergency Planning, Preparedness, and Response) Rules is vital for ensuring safety in handling hazardous materials used in fertiliser production. These regulations support the successful operation of SCU manufacturing facilities and enhance product safety and marketability.
Read more about this report - Request a Free Sample
| Report Features | Coverage - Detailed Report |
| Product Name | Sulphur Coated Urea |
| Report Coverage | Manufacturing Process & Unit Operations: In-depth analysis of each step involved in the production from raw materials, including technical tests, mass balance, and key unit operations. |
| Plant Infrastructure & Development: Comprehensive review of land selection, site development, environmental impacts, construction costs, and project phasing. | |
| Plant Layout & Design: Factors influencing the plant layout, including space planning, machinery placement, and operational efficiency. | |
| Machinery & Equipment Requirements: Analysis of machinery needs for production, including costs, suppliers, and technological advancements. | |
| Raw Material Procurement & Costs: Detailed breakdown of raw material requirements, procurement strategies, supplier options, and cost structures. | |
| Packaging & Distribution: Insight into packaging requirements, material selection, procurement channels, and associated costs. | |
| Operational Costs & Resources: Examination of utility needs (water, electricity), transportation logistics, human resources, and other operational costs. | |
| Financial & Economic Analysis: Project investment costs, financial projections, income/expenditure forecasts, and cost-benefit analysis. | |
| Profitability & Risk Analysis: Financial performance metrics, including profitability margins, payback period, and sensitivity to market risks. | |
| Market & Competitive Landscape: Competitive positioning, market trends, regional breakdown, and strategic recommendations for market growth. | |
| Currency | USD (Data can also be provided in the local currency) |
| Customization Scope | The report can also be customised based on the requirements of the customer |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 weeks of post-sale analyst support available. |
| Data Access | Lifetime Access |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
This prefeasibility report aims to equip potential investors and existing manufacturers with crucial insights to make informed decisions in the sulphur coated urea (SCU) industry.




*While we strive to always give you current and accurate information, the numbers depicted on the website are indicative and may differ from the actual numbers in the main report. At Expert Market Research, we aim to bring you the latest insights and trends in the market. Using our analyses and forecasts, stakeholders can understand the market dynamics, navigate challenges, and capitalize on opportunities to make data-driven strategic decisions.*
Get in touch with us for a customized solution tailored to your unique requirements and save upto 35%!
Basic Plan
USD 5,699
USD 4,844
Get Startedtax inclusive*
Raw Material and Product Specification, Raw material consumption, Process flow diagram
Machinery Cost, Working Capital
Utilities consumption, Operating cost, Overheads, Financing Charges, GSA , Packaging
Premium Plan
USD 6,799
USD 5,779
Get Startedtax inclusive*
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis
Raw material consumption and prices, Utilities consumption breakdown, By-Product Credit, Labour Charges Breakdown
Land and Site Cost, Equipment Cost, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Contingency, Engineering and Consulting Charges
Enterprise Plan
USD 8,899
USD 7,564
Get Startedtax inclusive*
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis, Variable Cost Breakdown, Investing Cost Breakdown,
Breakdown of machinery cost by equipment, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Piping, Electrical, Instrumentation
Cost of Construction, Plant Building, Site Development Charges
Land Cost, Development Charges
Dynamic Spreadsheet (Unlocked)
*Please note that the prices mentioned below are starting prices for each bundle type. Kindly contact our team for further details.*

Basic Plan
USD 5,699
USD 4,844
Key Processing Information
Raw Material and Product Specification, Raw Material Consumption, Process Flow Diagram
Capital Investment Analysis
Machinery Cost, Working Capital
Conversion Cost Analysis
Utilities Consumption, Operating Cost, Overheads, Financing Charges, GSA , Packaging

Premium Plan
USD 6,799
USD 5,779
All Contents of Basic Report
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis
Variable Cost Breakdown
Raw Material Consumption and Prices, Utilities Consumption, Breakdown By-Product Credit, Labour Charges Breakdown
Investing Cost Breakdown
Land and Site Cost, Equipment Cost, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Contingency, Engineering and Consulting Charges

Enterprise Plan
USD 8,899
USD 7,564
Includes all Report Content
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis, Variable Cost Breakdown, Investing Cost Breakdown,
Equipment Cost Breakdown
Breakdown of Machinery Cost By Equipment, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Piping, Electrical, Instrumentation
Land and Construction Cost Details
Land Cost, Development Charges, Cost of Construction, Plant Building, Site Development Charges
Dynamic Excel Cost Model
Dynamic Spreadsheet (Unlocked)
*Please note that the prices mentioned below are starting prices for each bundle type. Kindly contact our team for further details.*
Flash Bundle
Number of Reports: 3
20%
tax inclusive*
Small Business Bundle
Number of Reports: 5
25%
tax inclusive*
Growth Bundle
Number of Reports: 8
30%
tax inclusive*
Enterprise Bundle
Number of Reports: 10
35%
tax inclusive*
How To Order

Select License Type
Choose the right license for your needs and access rights.

Click on ‘Buy Now’
Add the report to your cart with one click and proceed to register.

Select Mode of Payment
Choose a payment option for a secure checkout. You will be redirected accordingly.
Gain insights to stay ahead and seize opportunities.
Get insights & trends for a competitive edge.
Track prices with detailed trend reports.
Analyse trade data for supply chain insights.

Leverage cost reports for smart savings
Enhance supply chain with partnerships.

Connect For More Information
Our expert team of analysts will offer full support and resolve any queries regarding the report, before and after the purchase.
Our expert team of analysts will offer full support and resolve any queries regarding the report, before and after the purchase.
We employ meticulous research methods, blending advanced analytics and expert insights to deliver accurate, actionable industry intelligence, staying ahead of competitors.
Our skilled analysts offer unparalleled competitive advantage with detailed insights on current and emerging markets, ensuring your strategic edge.
We offer an in-depth yet simplified presentation of industry insights and analysis to meet your specific requirements effectively.
Share