
Consumer Insights
Uncover trends and behaviors shaping consumer choices today
Procurement Insights
Optimize your sourcing strategy with key market data
Industry Stats
Stay ahead with the latest trends and market analysis.
The Expert Market Research report, titled “Cupric Sulfate Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2025 Edition: Industry Trends, Capital Investment, Price Trends, Manufacturing Process, Raw Materials Requirement, Plant Setup, Operating Cost, and Revenue Statistics” includes various aspects that are critical for establishing a cupric sulfate plant. These include infrastructure requirements, transportation requirements, utility specifications, and financial and economic analysis, among others.





The rising number of agricultural projects, particularly in emerging economies like India and China, has led to a surge in demand for cupric sulfate as a vital component in fertilisers, fungicides, and herbicides. In India, the Union Cabinet recently approved seven major agricultural projects with a combined investment of INR 13,966 crore aimed at advancing agricultural research and sustainable practices. Notable initiatives include the Digital Agriculture Mission, which focuses on integrating modern technologies into farming, and the Sustainable Development of Horticulture, which aims to enhance the cultivation of various crops including tropical and temperate varieties.
In 2024, the government allocated INR 3,979 crore for the Crop Science for Food and Nutritional Security project, highlighting research on pest control and crop improvement. This initiative is expected to drive significant demand for cupric sulfate as farmers seek effective solutions to protect their crops from diseases. Moreover, as these agricultural initiatives unfold, they are projected to boost overall agricultural output in India by approximately 4% annually, which will likely lead to increased consumption of cupric sulfate.
Other elements to consider while establishing a cupric sulfate plant include raw material sourcing, workforce planning, and packaging. The production of cupric sulfate relies on several key raw materials, such as copper ores and sulfuric acid, which are sourced from various mining and chemical processing industries. Copper ores, primarily mined in countries rich in mineral resources, serve as the primary source of copper for cupric sulfate production. These ores undergo processes like leaching or smelting to extract copper, which is then refined.
Sulfuric acid, another critical raw material, is typically produced through the Contact Process using sulfur dioxide derived from burning sulfur or metal sulfides. This acid is essential for reacting with copper to form cupric sulfate. These materials allow manufacturers to create cupric sulfate through methods such as dissolving copper scrap in dilute sulfuric acid or by oxidising copper sulfide ores. Hence, the sourcing and processing of these raw materials are vital for maintaining a steady supply of cupric sulfate.
Moreover, to help stakeholders determine the economics of a cupric sulfate plant, project funding, capital investments, and operating expenses are analyzed. Projections for income and expenditure, along with a detailed breakdown of fixed and variable costs, direct and indirect expenses, and profit and loss analysis, enable stakeholders to comprehend the financial health and sustainability of a business. These projections serve as a strategic tool for evaluating future profitability, assessing cash flow needs, and identifying potential financial risks.
However, challenges such as supply chain disruptions and logistical challenges may threaten supply stability. Factors like transportation delays and unexpected production stoppages can significantly impact the availability of raw materials needed for cupric sulfate production. To combat this, manufacturers of cupric sulfate can diversify their sourcing strategies by establishing relationships with multiple suppliers and investing in local production capabilities. This approach can mitigate supply chain risks by reducing dependency on single sources and enhancing resilience against unforeseen disruptions, ensuring a more stable supply of cupric sulfate in the market.
Cupric sulfate, also known as copper(II) sulfate (CuSO4), is a bright blue crystalline compound widely used in agriculture, chemistry, and medicine. Its most common form is the pentahydrate (CuSO4·5H2O), which appears as blue crystals and is used as a fungicide and herbicide. It can be synthesised by reacting copper oxide with sulfuric acid. Cupric sulfate is highly soluble in water and exhibits exothermic dissolution properties, which makes it valuable in various industrial applications. Historically, cupric sulfate was referred to as "blue vitriol," and was used in medicine and dyeing processes. However, its industrial significance grew during the 19th century with advancements in chemical manufacturing.
Cupric sulfate (CuSO4) appears as blue crystalline solids in its pentahydrate form (CuSO4·5H2O), with a molar mass of 249.685 g/mol, and as a grayish-white powder in its anhydrous form, which has a molar mass of 159.609 g/mol. The density of the hydrated form is approximately 2.286 g/cm³, while the anhydrous form has a density of about 3.6 g/cm³. The melting point of cupric sulfate pentahydrate is around 110 °C, and it loses water to become anhydrous at approximately 65 °C. Chemically, cupric sulfate is a powerful oxidising agent, highly soluble in water (about 31.6 g/100 mL at 20 °C), and decomposes upon heating to yield cupric oxide (CuO) and sulfur trioxide (SO3) at temperatures above 650 °C.
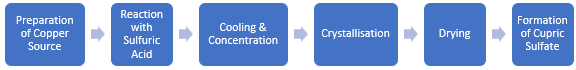
The production of cupric sulfate (CuSO4) begins with the preparation of a copper source, typically metallic copper, or copper oxide. The process starts by reacting copper with concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) at approximately 200 °C, resulting in the formation of cupric sulfate, water, and sulfur dioxide. After the initial reaction, the resulting solution is cooled to around 180-185 °F (82-85 °C) to facilitate further processing. The concentration of the solution may be adjusted by adding more sulfuric acid as necessary. Subsequently, the solution is allowed to cool further, promoting the crystallisation of cupric sulfate. The formed crystals are then filtered out and dried to obtain either the pentahydrate form (CuSO4·5H2O), which contains five water molecules, or the anhydrous form, depending on the drying conditions. Finally, the dried cupric sulfate is packaged for distribution.
Read more about this report - REQUEST FREE SAMPLE COPY IN PDF
The primary process of making cupric sulfate involves reacting copper with sulfuric acid in the presence of oxygen. This leads to the formation of cupric sulfate (CuSO4), water (H2O), and other by-products. Below is the step-by-step process:
1. Raw Materials:
2. Oxidation of Copper:
Cu (s) + O2 (g) → CuO (s)
In this step, copper (Cu) reacts with oxygen (O2) from the air to form copper oxide (CuO).
3. Reaction of Copper Oxide with Sulfuric Acid:
CuO (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → CuSO4 (aq) + H2O (l)
Copper oxide (CuO) then reacts with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) to produce cupric sulfate (CuSO4) and water (H2O).
4. Alternate Reaction (Direct Method):
In some industrial processes, copper metal can directly react with sulfuric acid in the presence of oxygen, bypassing the oxidation step:
2 Cu (s) + 2 H2SO4 (aq) + O2 (g) → 2 CuSO4 (aq) + 2 H2O (l)
This reaction produces cupric sulfate and water directly.
5. Crystallisation:
The resulting cupric sulfate solution is then concentrated by evaporation. Upon cooling, the CuSO4 crystallises, often in the form of blue pentahydrate crystals (CuSO4·5H2O).
6. Final Reaction (Hydration):
CuSO4 (s) + 5 H2O (l) → CuSO4·5H2O (s)
Cupric sulfate absorbs water molecules to form the hydrated form, cupric sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4·5H2O), which is the common blue crystalline form.
The cupric sulfate market is driven by diverse applications across agriculture, healthcare, and mining industries. In agriculture, cupric sulfate is a key component in fungicides and herbicides, effectively controlling over 300 plant diseases, including those affecting vineyards and citrus fruits. Approximately, 75% of the world's consumption of copper sulfate, estimated at around 200,000 tons annually, is used in agricultural practices to enhance crop yields and soil fertility. For instance, its use in Bordeaux mixture helps prevent fungal infections in crops like grapes and melons. In healthcare, its antimicrobial properties are leveraged in wound care; studies have shown that cupric sulfate can reduce infection rates significantly when used in treatments for skin infections. Additionally, in the mining industry, cupric sulfate serves as a flotation agent to enhance mineral extraction efficiency, particularly for lead and zinc ores.
Recent trends also indicate that the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) are experiencing rapid growth in copper sulfate applications for water treatment due to increasing concerns over water quality and scarcity. According to the UN World Water Development Report 2024, approximately 83% of the population in the MENA region is exposed to extremely high water stress, with countries like Bahrain, Kuwait, and Qatar facing critical shortages. By 2050, it is projected that 100% of the MENA population will experience extreme water stress. In response to these challenges, governments are increasingly using copper sulfate for its efficacy in treating water quality issues, such as controlling algal blooms. For instance, in 2024, it was reported that municipalities in regions like Saudi Arabia are implementing copper sulfate treatments to manage freshwater resources more sustainably.
A detailed overview of production cost analysis that evaluates the manufacturing process of cupric sulfate is crucial for stakeholders considering entry into this sector. Furthermore, stakeholders can make informed decisions based on the latest economic data, technological innovations, production process, requirements of raw materials, utility and operating costs, capital investments by major players, pricing strategies, and profit margins.
Below are the sections that further detail the comprehensive scope of the prefeasibility report for a cupric sulfate production plant:
Market Dynamics and Trends: Factors such as expanding use in water treatment processes are significantly affecting market conditions in the cupric sulfate sector. With the rising global demand for clean and safe drinking water, cupric sulfate serves as an effective algaecide that helps control algae growth in water bodies. This application is especially vital in areas facing water scarcity and quality issues, where maintaining clean water sources is crucial for public health. According to the 2024 UN World Water Development Report, approximately 2.2 billion people worldwide lack access to safely managed drinking water, with four billion experiencing severe water scarcity for at least one month each year.
Municipal and industrial water treatment facilities are increasingly turning to cupric sulfate to address these challenges. Notable projects include the Water Treatment Plant Upgrade Project in California, which aims to enhance the capacity and efficiency of local water treatment processes, and the National Water Quality Initiative in India, focusing on improving water quality in rural areas. These initiatives drive the demand for cupric sulfate as a reliable solution for maintaining water quality. Understanding these demands and trends helps businesses align their production plans in the cupric sulfate market.
Profiling of Key Industry Players: Leading manufacturers in the production of cupric sulfate include Atotech, Noah Chemicals, Wego Chemical Group, and Allan Chemical Corporation. Recently, these companies have been focusing on expanding their production capabilities to meet the increasing global demand for copper sulfate in agriculture and water treatment. Atotech has been enhancing its manufacturing processes to ensure compliance with international quality standards, while Noah Chemicals has expanded its facility to increase output and support the growing market needs.
Economic Analysis: Capital expenditure (CAPEX) analysis provides stakeholders the knowledge about required investments in advanced technologies, efficient machinery, and necessary infrastructure. Investing in high-capacity mixing equipment, such as a continuous mixer or high-shear mixer, can improve production efficiency by 20-30%. Investing in energy-efficient systems, such as combined heat and power (CHP) systems could reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, as these systems use waste heat from production processes to generate electricity and provide heating.
Fluctuations in cupric sulfate prices are influenced by raw material costs, production fluctuations, and geopolitical influences. The prices of essential feedstocks, particularly copper, directly impact cupric sulfate production costs. As of January 2025, copper prices are nearing a one-month high at approximately USD 4.29 per pound. The demand for cupric sulfate in agriculture and water treatment also affects pricing. During peak agricultural seasons, demand rises sharply, leading to potential price increases if supply does not keep pace. Reduced demand during off-peak seasons can lower prices. Geopolitical factors also play a critical role; disruptions in copper-producing regions due to trade disputes or conflicts can lead to supply chain challenges and increased costs. These elements contribute to a dynamic pricing environment for cupric sulfate.
Establishing a cupric sulfate manufacturing facility requires a comprehensive financial investment that encompasses various elements critical to the project's success. The following sections detail these components:
Projected profit margins and effective product pricing strategies improve overall profitability. Manufacturers might target a profit margin of around 20-30%, achieved through strategic pricing based on raw material costs and prevailing market demand. Effective pricing strategies should consider fluctuations in raw material prices and competitive positioning within the market.
The establishment of a cupric sulfate manufacturing facility must comply with various regulatory frameworks that govern production standards. Key regulations include the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines, which set permissible exposure limits for copper dust and fumes to ensure worker safety. Additionally, facilities must adhere to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations, particularly those related to hazardous substances under the Clean Water Act, which governs the discharge of pollutants and requires proper management of waste materials.
Manufacturers are also required to follow labelling and documentation standards, such as marking each container of copper sulfate solution with its measured specific gravity, pH value, and bottling date, as outlined by UL Standards. This ensures that all products meet safety and quality specifications before being distributed. Furthermore, compliance with local and international chemical safety regulations is essential to mitigate risks associated with handling cupric sulfate.
This prefeasibility report aims to equip potential investors and existing manufacturers with crucial insights to make informed decisions in the cupric sulfate industry.
*While we strive to always give you current and accurate information, the numbers depicted on the website are indicative and may differ from the actual numbers in the main report. At Expert Market Research, we aim to bring you the latest insights and trends in the market. Using our analyses and forecasts, stakeholders can understand the market dynamics, navigate challenges, and capitalize on opportunities to make data-driven strategic decisions.*
Get in touch with us for a customized solution tailored to your unique requirements and save upto 35%!
Basic Plan
USD 2,699
USD 2,429
Get Startedtax inclusive*
Raw Material and Product Specification, Raw material consumption, Process flow diagram
Machinery Cost, Working Capital
Utilities consumption, Operating cost, Overheads, Financing Charges, GSA , Packaging
Premium Plan
USD 3,699
USD 3,329
Get Startedtax inclusive*
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis
Raw material consumption and prices, Utilities consumption breakdown, By-Product Credit, Labour Charges Breakdown
Land and Site Cost, Equipment Cost, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Contingency, Engineering and Consulting Charges
Enterprise Plan
USD 4,799
USD 4,079
Get Startedtax inclusive*
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis, Variable Cost Breakdown, Investing Cost Breakdown,
Breakdown of machinery cost by equipment, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Piping, Electrical, Instrumentation
Cost of Construction, Plant Building, Site Development Charges
Land Cost, Development Charges
Dynamic Spreadsheet (Unlocked)
*Please note that the prices mentioned below are starting prices for each bundle type. Kindly contact our team for further details.*

Basic Plan
USD 2,699
USD 2,429
Key Processing Information
Raw Material and Product Specification, Raw Material Consumption, Process Flow Diagram
Capital Investment Analysis
Machinery Cost, Working Capital
Conversion Cost Analysis
Utilities Consumption, Operating Cost, Overheads, Financing Charges, GSA , Packaging

Premium Plan
USD 3,699
USD 3,329
All Contents of Basic Report
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis
Variable Cost Breakdown
Raw Material Consumption and Prices, Utilities Consumption, Breakdown By-Product Credit, Labour Charges Breakdown
Investing Cost Breakdown
Land and Site Cost, Equipment Cost, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Contingency, Engineering and Consulting Charges

Enterprise Plan
USD 4,799
USD 4,079
Includes all Report Content
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis, Variable Cost Breakdown, Investing Cost Breakdown,
Equipment Cost Breakdown
Breakdown of Machinery Cost By Equipment, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Piping, Electrical, Instrumentation
Land and Construction Cost Details
Land Cost, Development Charges, Cost of Construction, Plant Building, Site Development Charges
Dynamic Excel Cost Model
Dynamic Spreadsheet (Unlocked)
*Please note that the prices mentioned below are starting prices for each bundle type. Kindly contact our team for further details.*
Flash Bundle
Number of Reports: 3
20%
tax inclusive*
Small Business Bundle
Number of Reports: 5
25%
tax inclusive*
Growth Bundle
Number of Reports: 8
30%
tax inclusive*
Enterprise Bundle
Number of Reports: 10
35%
tax inclusive*
How To Order
Our step-by-step guide will help you select, purchase, and access your reports swiftly, ensuring you get the information that drives your decisions, right when you need it.

Select License Type
Choose the right license for your needs and access rights.

Click on ‘Buy Now’
Add the report to your cart with one click and proceed to register.

Select Mode of Payment
Choose a payment option for a secure checkout. You will be redirected accordingly.
Gain insights to stay ahead and seize opportunities.
Get insights & trends for a competitive edge.
Track prices with detailed trend reports.
Analyse trade data for supply chain insights.

Leverage cost reports for smart savings
Enhance supply chain with partnerships.

Connect For More Information
Our expert team of analysts will offer full support and resolve any queries regarding the report, before and after the purchase.
Our expert team of analysts will offer full support and resolve any queries regarding the report, before and after the purchase.
We employ meticulous research methods, blending advanced analytics and expert insights to deliver accurate, actionable industry intelligence, staying ahead of competitors.
Our skilled analysts offer unparalleled competitive advantage with detailed insights on current and emerging markets, ensuring your strategic edge.
We offer an in-depth yet simplified presentation of industry insights and analysis to meet your specific requirements effectively.


Australia
63 Fiona Drive, Tamworth, NSW
+61-448-061-727
India
C130 Sector 2 Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301
+91-723-689-1189
Philippines
40th Floor, PBCom Tower, 6795 Ayala Avenue Cor V.A Rufino St. Makati City,1226.
+63-287-899-028, +63-967-048-3306
United Kingdom
6 Gardner Place, Becketts Close, Feltham TW14 0BX, Greater London
+44-753-713-2163
United States
30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801
+1-415-325-5166
Vietnam
193/26/4 St.no.6, Ward Binh Hung Hoa, Binh Tan District, Ho Chi Minh City
+84-865-399-124
United States (Head Office)
30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801
+1-415-325-5166
Australia
63 Fiona Drive, Tamworth, NSW
+61-448-061-727
India
C130 Sector 2 Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301
+91-723-689-1189
Philippines
40th Floor, PBCom Tower, 6795 Ayala Avenue Cor V.A Rufino St. Makati City, 1226.
+63-287-899-028, +63-967-048-3306
United Kingdom
6 Gardner Place, Becketts Close, Feltham TW14 0BX, Greater London
+44-753-713-2163
Vietnam
193/26/4 St.no.6, Ward Binh Hung Hoa, Binh Tan District, Ho Chi Minh City
+84-865-399-124
Share