
Consumer Insights
Uncover trends and behaviors shaping consumer choices today
Procurement Insights
Optimize your sourcing strategy with key market data
Industry Stats
Stay ahead with the latest trends and market analysis.
The Expert Market Research report, titled “Corn Cob Based Bioplastic Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2025 Edition: Industry Trends, Capital Investment, Price Trends, Manufacturing Process, Raw Materials Requirement, Plant Setup, Operating Cost, and Revenue Statistics” includes various aspects that are critical for establishing a corn cob based bioplastic plant. These include infrastructure requirements, transportation requirements, utility specifications, and financial and economic analysis, among others.





The demand for corn cob-based bioplastics is rising due to the urgent need for sustainable alternatives to traditional plastics. As consumers and businesses become more conscious of plastic pollution and its harmful effects, they are actively seeking biodegradable options. For instance, companies like NatureWorks produce Ingeo™, a biopolymer derived from corn starch that can be used in various applications, including food packaging and disposable cutlery. Corn cob bioplastics decompose within 90 to 180 days under composting conditions, presenting a compelling solution to the plastic waste crisis. Additionally, using agricultural residues like corn cobs as a renewable resource reduces reliance on fossil fuels and contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions, potentially by up to 68% compared to conventional plastics.
Government initiatives and regulations further bolster the market for corn cob-based bioplastics by promoting eco-friendly practices and providing incentives for manufacturers. For example, the European Union's directives on reducing single-use plastics have encouraged companies to explore alternatives like bioplastics. These materials are finding applications in packaging, automotive components, and disposable products. As technological advancements improve their durability and heat resistance, corn cob bioplastics are becoming suitable for a broader range of uses. These factors create a favourable landscape for the expansion of corn cob-based bioplastics in the marketplace.
Other elements to consider while establishing a corn cob based bioplastic plant include raw material sourcing, workforce planning, and packaging. The production of corn cob-based bioplastics relies on corn cobs, which are sourced from agricultural residues. Corn cobs are rich in cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, making them an ideal feedstock for creating biodegradable plastics. For instance, they can be processed into granules that are then blended with biodegradable polymers like polylactic acid (PLA) to produce bio-composites with enhanced performance properties. This process contributes to waste reduction in the agricultural sector.
Other raw materials such as furfural and carbon dioxide (CO2) can be derived from corn cobs to create advanced bioplastics. The conversion process involves transforming corncobs into furfural, which is then used to produce furoic acid—a common food additive. This furoic acid can be mixed with CO2 to produce 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA), a precursor for polyethylene furandicarboxylate (PEF), which serves as a promising alternative to traditional PET plastics. This highlights the versatility of corn cobs in bioplastic production.
Moreover, to help stakeholders determine the economics of a corn cob based bioplastic plant, project funding, capital investments, and operating expenses are analyzed. Projections for income and expenditure, along with a detailed breakdown of fixed and variable costs, direct and indirect expenses, and profit and loss analysis, enable stakeholders to comprehend the financial health and sustainability of a business. These projections serve as a strategic tool for evaluating future profitability, assessing cash flow needs, and identifying potential financial risks.
However, challenges such as seasonal availability, logistical difficulties, and storage issues may threaten supply stability for corn cob-based bioplastics. Corn cobs are harvested during specific months, leading to irregular supply outside the harvest period. In India, for example, the fragmented nature of smallholder farms complicates the collection and transportation of cobs to processing units, while inadequate storage facilities result in post-harvest losses of up to 10-15% due to moisture and pests. Additionally, low farmer awareness about the economic potential of corn cobs as a feedstock limits large-scale collection and use.
To combat these challenges, manufacturers of corn cob-based bioplastics can establish strategic partnerships with local farmers and invest in improved storage and transportation infrastructure. By creating cooperative models that incentivise farmers to produce and supply corn cobs year-round, manufacturers can mitigate supply chain risks. Implementing better storage solutions, such as climate-controlled facilities, would help preserve the quality of corn cobs and reduce losses during the off-season. These strategies ensure a more stable supply of raw materials and improves the overall sustainability of the corn cob bioplastic production process.
Bioplastics derived from corn cobs are made from renewable agricultural residues, which significantly reduces reliance on fossil fuels and reduces plastic pollution. Corn cob bioplastics find applications in packaging, automotive components, and more, while producing fewer greenhouse gases during manufacturing compared to conventional plastics. In 1989, Cargill chemist Patrick Gruber developed a more efficient method for producing polylactic acid (PLA) from corn, which is even used today.
Corn cob-based bioplastics are biodegradable and can decompose within 90 to 180 days under composting conditions. They exhibit a hardness comparable to iron, rated at approximately 4.5 on the Mohs scale, and have controlled particle sizes typically ranging from 50 to 200 micrometers. The tensile strength of these bioplastics can vary around 6.50 MPa when reinforced with additives like carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) at a concentration of 60% w/w starch.
Chemically, corn cobs are composed of about 40-44% cellulose, 31-33% hemicellulose, and 16-18% lignin, which adds to their mechanical strength and thermal stability. Moreover, the addition of titanium dioxide (TiO2) at concentrations such as 1% to 2%, can enhance antibacterial properties, making these bioplastics suitable for food packaging applications as well. Furthermore, the flexural strength of bioplastics ranges from 69.9 MPa for untreated corncobs to 105.6 MPa for silane-treated corncobs, which indicates a 51% increase in strength due to improved interfacial bonding within the matrix.
The production of corn cob-based bioplastics begins with the collection of corn cobs as the primary feedstock. The cobs are then washed to remove impurities and dried for 24 hours to ensure moisture removal. Following this, they are ground and sieved to obtain flour with a particle size of 100 mesh.
Next, starch isolation takes place by soaking the corn cob flour in distilled water for 24 hours, followed by filtration to separate the starch residue from the pulp. The starch is then dried at 100°C to yield flour. The subsequent step involves preparing a bioplastic mixture, where 2 grams of corn cob starch are dissolved in 75 ml of distilled water, combined with a Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) solution at varying concentrations (20% to 60% w/w). This CMC solution is heated at 75°C for 30 minutes to activate its properties.
The two solutions are then mixed and heated at 80°C for 15 minutes to create a homogeneous blend. This mixture is poured into moulds measuring approximately 20 cm x 15 cm and dried in an oven at 70°C for 7 hours until it becomes firm. Finally, the dried bioplastic is released from the mould, resulting in corn cob based bioplastic.

Read more about this report - REQUEST FREE SAMPLE COPY IN PDF
Corn cob-based bioplastic market growth is being driven by the increasing demand for sustainable alternatives to traditional plastics. These bioplastics are used in diverse applications, including packaging materials, disposable cutlery, and food containers, which help reduce reliance on single-use plastics. For example, corn cob bioplastics can replace conventional polystyrene in food packaging, significantly reducing waste. Additionally, research shows that incorporating lignin-containing cellulose nanofibrils (LCNF) can enhance the mechanical properties of bioplastics, making them suitable for automotive components, where they can withstand temperatures up to 80°C. Government initiatives also play a crucial role; for instance, the U.S. Department of Agriculture promotes the use of agricultural residues like corn cobs to support sustainable manufacturing practices. Furthermore, studies indicate that bioplastics derived from corn cobs can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 68% compared to traditional plastics. Moreover, the moisture content of these bioplastics is typically less than 10%, which improves their stability and usability in various applications, leading to further growth in the market.
A detailed overview of production cost analysis that evaluates the manufacturing process of corn cob based bioplastic is crucial for stakeholders considering entry into this sector. Furthermore, stakeholders can make informed decisions based on the latest economic data, technological innovations, production process, requirements of raw materials, utility and operating costs, capital investments by major players, pricing strategies, and profit margins. For instance, PlantSwitch has raised USD 8 million to establish a new 52,000-square-foot manufacturing facility in Sanford, North Carolina, which is expected to produce over 50 million pounds (approximately 22,000 tonnes) of bioplastic resin annually. The company uses agricultural waste, including corn cobs, to create a low-cost, compostable plastic alternative that decomposes in countertop compost machines within eight hours and within three months in commercial composting conditions. Similarly, the Kerala Irrigation Infrastructure Development Corporation Ltd (KIIDC) plans to replace traditional plastic bottles with bioplastic bottles made from polylactic acid (PLA), derived from starches found in corn. These transparent bottles will decompose in soil within six months and will not cause environmental pollution when incinerated. As more companies and institutions aim to replace all petroleum-based single-use plastics with plant-based materials, production outlook of corn cob based bioplastic seems favourable.
Below are the sections that further detail the comprehensive scope of the prefeasibility report for a corn cob based bioplastic production plant:
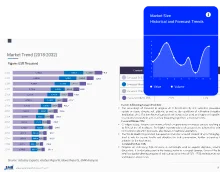
Market Dynamics and Trends: Factors such as steady corn production are significantly affecting market conditions in the corn cob-based bioplastic sector. In the 2024/25 season, global corn production is forecasted to reach approximately 1.219 billion metric tons. The United States will be the largest producer, with projected production at about 384.6 million metric tons. China is expected to produce around 292 million metric tons, marking a 1.1% increase, while Brazil anticipates a production of approximately 127 million metric tons, representing a growth of 4.1%. The European Union's total corn production is forecasted at 58 million metric tons. Notably, Romania reports a cultivated area for corn reaching about 2.259 million hectares as of December 2024, while France has approximately 1.611 million hectares dedicated to grain maize and corn-cob-mix during the same period. The forecasted rise in corn production globally presents an opportunity for the corn cob-based bioplastic market to expand significantly.
Profiling of Key Industry Players: Leading manufacturers included in the corn cob-based bioplastic report are NatureWorks LLC, TotalEnergies Corbion, and Plantic Technologies. Recently, these companies have been making significant strides in enhancing their product offerings and expanding their market reach. For example, NatureWorks LLC is known for its Ingeo biopolymer, which is derived from renewable resources like corn and is used in various applications, including food packaging and disposable cutlery. TotalEnergies Corbion has also been actively developing high-quality polylactic acid (PLA) bioplastics. Additionally, Plantic Technologies produces fully biodegradable materials from corn for eco-friendly packaging solutions. These efforts underscore a growing commitment among leading manufacturers in the corn cob-based bioplastic sector.
Economic Analysis: Capital expenditure (CAPEX) analysis provides stakeholders the knowledge about required investments in advanced technologies, efficient machinery, and necessary infrastructure. Investing in high-capacity mixing equipment, such as a continuous mixer or high-shear mixer, can improve production efficiency by 20-30%. Investing in energy-efficient systems, such as combined heat and power (CHP) systems could reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, as these systems use waste heat from production processes to generate electricity and provide heating.
Historical, Current, and Forecasted Price Trends
Fluctuations in corn cob-based bioplastic prices are influenced by raw material costs, production technology, and market demand. The price of corn cobs, as a primary feedstock, can vary significantly based on agricultural yields and seasonal availability. For instance, during peak harvest seasons, the abundance of corn cobs may lead to lower prices, while off-season scarcity can drive costs up. Additionally, the production of corn cob-based bioplastics often involves more complex manufacturing processes compared to traditional plastics, resulting in higher operational costs that can impact pricing. Reports indicate that biodegradable plastics, including those made from corn cobs, can be approximately 30-50% more expensive than conventional plastics due to these factors.
Government policies also affect the pricing of corn cob-based bioplastics through various mechanisms that promote sustainability and reduce reliance on traditional plastics. For instance, regulations such as bans on single-use plastics and mandatory quotas for bioplastic content in certain products can stimulate demand for corn cob-based alternatives. These policies encourage manufacturers to invest in bioplastic production, which can lead to economies of scale and potentially lower prices over time.
Moreover, policies that support research and development in bioplastics technology can lead to innovations that enhance the properties of corn cob-based materials, thereby increasing their market appeal. Conversely, if government policies shift away from supporting renewable materials or if subsidies are reduced, it could lead to increased costs for manufacturers and higher prices for consumers. These market conditions shape the pricing landscape for corn cob-based bioplastics.
Establishing a corn cob based bioplastic manufacturing facility requires a comprehensive financial investment that encompasses various elements critical to the project's success. The following sections detail these components:
Projected profit margins and effective product pricing strategies improve overall profitability. Manufacturers might target a profit margin of around 20-30%, achieved through strategic pricing based on raw material costs and prevailing market demand. Effective pricing strategies should consider fluctuations in raw material prices and competitive positioning within the market.
The production of corn cob-based bioplastics is governed by several key regulatory frameworks, including environmental regulations, food safety standards, and bioplastic certifications. Manufacturers must comply with local and national environmental laws, such as conducting Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) to evaluate the ecological impact of their operations and adhering to waste management and emissions standards set by agencies like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Additionally, because these bioplastics are often used in food packaging, they must meet stringent safety regulations established by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Furthermore, obtaining certifications from organizations like the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) or ASTM International can enhance product credibility by demonstrating compliance with specific biodegradability and compostability standards. These frameworks ensure that corn cob-based bioplastics are safe for consumers and the environment.
This prefeasibility report aims to equip potential investors and existing manufacturers with crucial insights to make informed decisions in the corn cob based bioplastic industry.
*While we strive to always give you current and accurate information, the numbers depicted on the website are indicative and may differ from the actual numbers in the main report. At Expert Market Research, we aim to bring you the latest insights and trends in the market. Using our analyses and forecasts, stakeholders can understand the market dynamics, navigate challenges, and capitalize on opportunities to make data-driven strategic decisions.*
Get in touch with us for a customized solution tailored to your unique requirements and save upto 35%!
Basic Plan
USD 2,699
USD 2,429
Get Startedtax inclusive*
Raw Material and Product Specification, Raw material consumption, Process flow diagram
Machinery Cost, Working Capital
Utilities consumption, Operating cost, Overheads, Financing Charges, GSA , Packaging
Premium Plan
USD 3,699
USD 3,329
Get Startedtax inclusive*
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis
Raw material consumption and prices, Utilities consumption breakdown, By-Product Credit, Labour Charges Breakdown
Land and Site Cost, Equipment Cost, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Contingency, Engineering and Consulting Charges
Enterprise Plan
USD 4,799
USD 4,079
Get Startedtax inclusive*
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis, Variable Cost Breakdown, Investing Cost Breakdown,
Breakdown of machinery cost by equipment, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Piping, Electrical, Instrumentation
Cost of Construction, Plant Building, Site Development Charges
Land Cost, Development Charges
Dynamic Spreadsheet (Unlocked)
*Please note that the prices mentioned below are starting prices for each bundle type. Kindly contact our team for further details.*

Basic Plan
USD 2,699
USD 2,429
Key Processing Information
Raw Material and Product Specification, Raw Material Consumption, Process Flow Diagram
Capital Investment Analysis
Machinery Cost, Working Capital
Conversion Cost Analysis
Utilities Consumption, Operating Cost, Overheads, Financing Charges, GSA , Packaging

Premium Plan
USD 3,699
USD 3,329
All Contents of Basic Report
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis
Variable Cost Breakdown
Raw Material Consumption and Prices, Utilities Consumption, Breakdown By-Product Credit, Labour Charges Breakdown
Investing Cost Breakdown
Land and Site Cost, Equipment Cost, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Contingency, Engineering and Consulting Charges

Enterprise Plan
USD 4,799
USD 4,079
Includes all Report Content
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis, Variable Cost Breakdown, Investing Cost Breakdown,
Equipment Cost Breakdown
Breakdown of Machinery Cost By Equipment, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Piping, Electrical, Instrumentation
Land and Construction Cost Details
Land Cost, Development Charges, Cost of Construction, Plant Building, Site Development Charges
Dynamic Excel Cost Model
Dynamic Spreadsheet (Unlocked)
*Please note that the prices mentioned below are starting prices for each bundle type. Kindly contact our team for further details.*
Flash Bundle
Number of Reports: 3
20%
tax inclusive*
Small Business Bundle
Number of Reports: 5
25%
tax inclusive*
Growth Bundle
Number of Reports: 8
30%
tax inclusive*
Enterprise Bundle
Number of Reports: 10
35%
tax inclusive*
How To Order
Our step-by-step guide will help you select, purchase, and access your reports swiftly, ensuring you get the information that drives your decisions, right when you need it.

Select License Type
Choose the right license for your needs and access rights.

Click on ‘Buy Now’
Add the report to your cart with one click and proceed to register.

Select Mode of Payment
Choose a payment option for a secure checkout. You will be redirected accordingly.
Gain insights to stay ahead and seize opportunities.
Get insights & trends for a competitive edge.
Track prices with detailed trend reports.
Analyse trade data for supply chain insights.

Leverage cost reports for smart savings
Enhance supply chain with partnerships.

Connect For More Information
Our expert team of analysts will offer full support and resolve any queries regarding the report, before and after the purchase.
Our expert team of analysts will offer full support and resolve any queries regarding the report, before and after the purchase.
We employ meticulous research methods, blending advanced analytics and expert insights to deliver accurate, actionable industry intelligence, staying ahead of competitors.
Our skilled analysts offer unparalleled competitive advantage with detailed insights on current and emerging markets, ensuring your strategic edge.
We offer an in-depth yet simplified presentation of industry insights and analysis to meet your specific requirements effectively.


Australia
63 Fiona Drive, Tamworth, NSW
+61-448-061-727
India
C130 Sector 2 Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301
+91-723-689-1189
Philippines
40th Floor, PBCom Tower, 6795 Ayala Avenue Cor V.A Rufino St. Makati City,1226.
+63-287-899-028, +63-967-048-3306
United Kingdom
6 Gardner Place, Becketts Close, Feltham TW14 0BX, Greater London
+44-753-713-2163
United States
30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801
+1-415-325-5166
Vietnam
193/26/4 St.no.6, Ward Binh Hung Hoa, Binh Tan District, Ho Chi Minh City
+84-865-399-124
United States (Head Office)
30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801
+1-415-325-5166
Australia
63 Fiona Drive, Tamworth, NSW
+61-448-061-727
India
C130 Sector 2 Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301
+91-723-689-1189
Philippines
40th Floor, PBCom Tower, 6795 Ayala Avenue Cor V.A Rufino St. Makati City, 1226.
+63-287-899-028, +63-967-048-3306
United Kingdom
6 Gardner Place, Becketts Close, Feltham TW14 0BX, Greater London
+44-753-713-2163
Vietnam
193/26/4 St.no.6, Ward Binh Hung Hoa, Binh Tan District, Ho Chi Minh City
+84-865-399-124
Share