
Consumer Insights
Uncover trends and behaviors shaping consumer choices today
Procurement Insights
Optimize your sourcing strategy with key market data
Industry Stats
Stay ahead with the latest trends and market analysis.
The Expert Market Research report, titled “Copper (II) Carbonate Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2025 Edition: Industry Trends, Capital Investment, Price Trends, Manufacturing Process, Raw Materials Requirement, Plant Setup, Operating Cost, and Revenue Statistics” includes various aspects that are critical for establishing a copper (II) carbonate plant. These include infrastructure requirements, transportation requirements, utility specifications, and financial and economic analysis, among others.





The demand for copper (II) carbonate is increasingly driven by the growing agricultural sectors in countries like India and China. Copper (II) carbonate is widely used in agriculture as a fungicide and wood preservative. In India, the total Kharif food grain production for 2024-25 is projected at 1,647.05 Lakh Metric Tons (LMT), representing an increase of 89.37 LMT compared to the previous year. This growth is attributed to favoruable weather conditions and improved agricultural practices, including the use of effective crop protection products like copper (II) carbonate, which helps enhance crop yields and protect against diseases. Similarly, in China, the agricultural sector is witnessing substantial growth, with total grain output projected to reach approximately 680 million tons in 2024. This growth is supported by increased investment in agricultural technology, expansion of arable land through improved irrigation practices, and the adoption of integrated pest management strategies that often include copper-based compounds. Both India and China are leveraging chemical inputs like copper (II) carbonate to improve crop health and yield, thereby driving up its demand in these rapidly growing markets.
Other elements to consider while establishing a copper (II) carbonate plant include raw material sourcing, workforce planning, and packaging. The production of copper (II) carbonate relies on several key raw materials, primarily copper salts and carbonate sources. Commonly used copper salts include copper(II) sulfate (CuSO4), which is frequently reacted with sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) to make copper (II) carbonate. Another important copper salt is copper(II) chloride (CuCl2), which can react with sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) to produce the same compound. These raw materials are essential for the effective synthesis of copper (II) carbonate, influencing both the yield and purity of the final product.
Moreover, to help stakeholders determine the economics of a copper (II) carbonate plant, project funding, capital investments, and operating expenses are analyzed. Projections for income and expenditure, along with a detailed breakdown of fixed and variable costs, direct and indirect expenses, and profit and loss analysis, enable stakeholders to comprehend the financial health and sustainability of a business. These projections serve as a strategic tool for evaluating future profitability, assessing cash flow needs, and identifying potential financial risks.
However, challenges such as supply and demand imbalances, environmental concerns, and geopolitical risks may threaten supply stability in the copper (II) carbonate market. The ageing of major copper mines and declining ore grades contribute to potential shortages, while trade tensions and political instability in key producing countries can further complicate supply chains. To combat these challenges, manufacturers can diversify their sourcing strategies by establishing relationships with multiple suppliers and investing in sustainable mining practices. This approach can mitigate supply chain risks by ensuring a more stable and responsible supply of raw materials, ultimately enhancing the resilience of the copper (II) carbonate market.
Basic copper carbonate, also known as copper (II) carbonate hydroxide, is a green solid that occurs naturally as the mineral malachite. It has been used since antiquity as a pigment, sometimes called verditer, green bice, or mountain green. The compound consists of copper (II) cations bonded to carbonate and hydroxide ions, with the common formulas Cu2(CO3) (OH)2 for malachite and Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2 for the blue mineral azurite. It is also used as a precursor for catalysts and in wood preservation. Additionally, it is involved in removing thiols and hydrogen sulfide from gas streams.
Historically, copper compounds like malachite and azurite have been important pigments since ancient times. In 1794, Joseph Louis Proust studied the thermal decomposition of copper carbonate. Basic copper carbonate is prepared by mixing aqueous solutions of copper (II) sulfate and sodium carbonate or sodium bicarbonate. The true neutral copper (II) carbonate CuCO3 was first reliably produced in 1973 by heating basic copper carbonate under high temperature and pressure.
Copper carbonate, with the chemical formula CuCO3, is a rare compound that is difficult to prepare and readily reacts with water moisture from the air. It is an ionic solid consisting of copper (II) cations Cu2+ and carbonate anions CO32-. The stability of dry CuCO3 depends critically on the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO2). It is stable for months in dry air but decomposes slowly into CuO and CO2 if pCO2 is less than 0.11 atm. In the presence of water or moist air at 25°C, CuCO3 is stable only for pCO2 above 4.57 atmospheres and pH between about 4 and 8. Below that partial pressure, it reacts with water to form a basic carbonate like malachite (Cu2(CO3) (OH)2) or azurite (Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2).
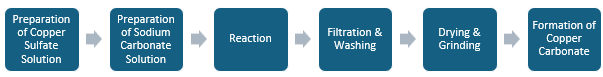
The manufacturing process of copper carbonate begins with the preparation of copper sulfate and sodium carbonate solutions, each dissolved in water to specific concentrations. These two solutions are then combined in a reactor, where they react under controlled conditions, maintaining a pH of 8.0 to 8.2 and a temperature of 30-50°C for 1-2 hours. After the reaction, the mixture is allowed to settle, and the precipitated copper carbonate is filtered and washed to remove sulfate ions. The resulting filter cake is then dried at 80 ± 3°C and ground to produce the final copper (II) carbonate product.
Read more about this report - REQUEST FREE SAMPLE COPY IN PDF
Copper carbonate (CuCO3) can be produced through several methods. Below is a description of one common method involving the precipitation process from a copper salt solution:
1. Raw Materials
The raw materials required to produce copper carbonate include:
2. Reaction Process
The basic reaction for producing copper carbonate can be represented by the reaction between copper sulfate (CuSO4) and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) in an aqueous medium. The general reaction is a double displacement reaction, resulting in the formation of copper carbonate (CuCO3) and sodium sulfate (Na2SO4).
The balanced chemical reaction is as follows:
CuSO4 + Na2CO3 → CuCO3 (precipitate) + Na2SO4
3. Detailed Process Steps
Step 1: Preparation of Copper Sulfate Solution
In the first step, copper sulfate (CuSO4) is dissolved in water to form a copper sulfate solution. The dissolution reaction is as follows:
CuSO4(s) + H2O → Cu(2+)(aq) + SO4(2-)(aq)
Step 2: Addition of Sodium Carbonate
Next, sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is added to the copper sulfate solution. Sodium carbonate dissociates into sodium ions (Na(+)) and carbonate ions (CO3(2-)) in the aqueous medium:
Na2CO3(s) → 2Na(+)(aq) + CO3(2-)(aq)
Step 3: Formation of Copper Carbonate
The carbonate ions (CO3(2-)) react with copper ions (Cu(2+)) to form copper carbonate (CuCO3), which precipitates out of the solution as a solid. The reaction is:
Cu(2+)(aq) + CO3(2-)(aq) → CuCO3(s)
Step 4: Separation and Drying
Once the copper carbonate precipitate forms, it is filtered out from the solution. The filtered copper carbonate is then dried to obtain the final product.
The global copper (II) carbonate market is driven by its diverse applications across various industries. In agriculture, copper carbonate is used as a fungicide for crops like wheat, barley, and oats, and as an ingredient in animal feed to promote healthy livestock growth. It is also used as a wood preservative, with copper carbonate added to arsenic to produce acetoarsenite (Paris green). In the food industry, copper carbonate powder is gaining attention for its potential as a food additive due to its antimicrobial properties and ability to extend shelf life. Copper carbonate is used in paints, varnishes, artist paints (known as verditer or mountain green), fireworks, and pottery glazes as a colouring agent. The rising demand for sustainable food production, growing awareness of copper's nutritional benefits, and technological advancements in food processing are further driving the market growth.
A detailed overview of production cost analysis that evaluates the manufacturing process of copper (II) carbonate is crucial for stakeholders considering entry into this sector. Furthermore, stakeholders can make informed decisions based on the latest economic data, technological innovations, production process, requirements of raw materials, utility and operating costs, capital investments by major players, pricing strategies, and profit margins. For instance, in December 2024, Norden Crown Metals Corp. has identified new copper porphyry and epithermal gold targets at the Smart Creek Gold-Copper Project in Montana. The recent discovery of new copper porphyry targets by Norden Crown Metals have significant implications for manufacturers in the copper(II) carbonate market. The potential increase in copper supply may lead to fluctuations in prices, impacting production costs for manufacturers like Eastmen Chemicals and Jost Chemical, who dominate the market. Additionally, the growing demand for copper(II) carbonate in industries such as agriculture and paints may further drive competition among suppliers.
Below are the sections that further detail the comprehensive scope of the prefeasibility report for a copper (II) carbonate production plant:
Market Dynamics and Trends: Growth factors such as increasing demand in electronics are significantly affecting market conditions in the copper (II) carbonate sector. As a potential anode material for lithium-ion batteries, it has garnered interest due to its high initial discharge capacity. This application aligns with the global push towards renewable energy solutions and electric vehicles, further propelling the market for copper (II) carbonate. In 2024, the demand for electric vehicles (EVs) is expected to reach approximately 14 million units. The solar power industry is projected to expand with an installed capacity of around 1,200 gigawatts (GW), while wind power applications are anticipated to grow to about 1,000 GW of installed capacity. These trends indicate the importance of copper (II) carbonate. Understanding these factors helps businesses align their production plans with demands and trends in the copper (II) carbonate market.
Profiling of Key Industry Players: Leading manufacturers like Fengchen Group, Meghachem, CDH Fine Chemicals, and Todini Chemicals are included in the copper (II) carbonate report. Recently, Nasit Pharmachem has also gained recognition as a notable supplier of high-quality copper carbonate products in India. Additionally, companies such as Vetrivel Chemicals, Anusari Chemical, and Sam Industries are contributing to the sector by providing various grades of copper (II) carbonate for applications in agriculture, electronics, and chemical industries. This group of manufacturers enhances the overall market landscape by ensuring a steady supply of copper (II) carbonate.
Economic Analysis: Capital expenditure (CAPEX) analysis provides stakeholders the knowledge about required investments in advanced technologies, efficient machinery, and necessary infrastructure. Investing in high-capacity mixing equipment, such as a continuous mixer or high-shear mixer, can improve production efficiency by 20-30%. Investing in energy-efficient systems, such as combined heat and power (CHP) systems could reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, as these systems use waste heat from production processes to generate electricity and provide heating.
Fluctuations in copper (II) carbonate prices are influenced by the costs of essential raw materials such as copper salts and carbonate sources. The primary raw materials include copper(II) sulfate (CuSO4) and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), which are crucial for the manufacturing process. Additionally, the availability and pricing of these raw materials can be affected by market dynamics, including mining output, transportation costs, and geopolitical factors. Any disruptions in the supply chain or changes in production levels from major copper-producing countries can lead to significant price volatility. Manufacturers must closely monitor these fluctuations to manage their production costs effectively and maintain competitive pricing in the market.
Establishing a copper (II) carbonate manufacturing facility requires a comprehensive financial investment that encompasses various elements critical to the project's success. The following sections detail these components:
Projected profit margins and effective product pricing strategies improve overall profitability. Manufacturers might target a profit margin of around 20-30%, achieved through strategic pricing based on raw material costs and prevailing market demand. Effective pricing strategies should consider fluctuations in raw material prices and competitive positioning within the market.
The establishment of a copper (II) carbonate manufacturing facility must comply with various regulatory frameworks that govern production standards. Key regulations include Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH), which mandates the registration, evaluation, authorization, and restriction of chemicals within the European Union. This regulation requires manufacturers to provide comprehensive safety data related to the handling and use of copper (II) carbonate, ensuring that potential health and environmental risks are adequately assessed and managed. Additionally, compliance with local environmental regulations is essential, which may involve obtaining permits for emissions and waste management. Manufacturers must also adhere to occupational safety standards that protect workers from exposure to harmful substances associated with copper (II) carbonate production. Compliance with these regulations not only ensures legal operation but also enhances product safety and marketability.
This prefeasibility report aims to equip potential investors and existing manufacturers with crucial insights to make informed decisions in the copper (II) carbonate industry.
*While we strive to always give you current and accurate information, the numbers depicted on the website are indicative and may differ from the actual numbers in the main report. At Expert Market Research, we aim to bring you the latest insights and trends in the market. Using our analyses and forecasts, stakeholders can understand the market dynamics, navigate challenges, and capitalize on opportunities to make data-driven strategic decisions.*
Get in touch with us for a customized solution tailored to your unique requirements and save upto 35%!
Basic Plan
USD 2,699
USD 2,429
Get Startedtax inclusive*
Raw Material and Product Specification, Raw material consumption, Process flow diagram
Machinery Cost, Working Capital
Utilities consumption, Operating cost, Overheads, Financing Charges, GSA , Packaging
Premium Plan
USD 3,699
USD 3,329
Get Startedtax inclusive*
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis
Raw material consumption and prices, Utilities consumption breakdown, By-Product Credit, Labour Charges Breakdown
Land and Site Cost, Equipment Cost, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Contingency, Engineering and Consulting Charges
Enterprise Plan
USD 4,799
USD 4,079
Get Startedtax inclusive*
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis, Variable Cost Breakdown, Investing Cost Breakdown,
Breakdown of machinery cost by equipment, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Piping, Electrical, Instrumentation
Cost of Construction, Plant Building, Site Development Charges
Land Cost, Development Charges
Dynamic Spreadsheet (Unlocked)
*Please note that the prices mentioned below are starting prices for each bundle type. Kindly contact our team for further details.*

Basic Plan
USD 2,699
USD 2,429
Key Processing Information
Raw Material and Product Specification, Raw Material Consumption, Process Flow Diagram
Capital Investment Analysis
Machinery Cost, Working Capital
Conversion Cost Analysis
Utilities Consumption, Operating Cost, Overheads, Financing Charges, GSA , Packaging

Premium Plan
USD 3,699
USD 3,329
All Contents of Basic Report
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis
Variable Cost Breakdown
Raw Material Consumption and Prices, Utilities Consumption, Breakdown By-Product Credit, Labour Charges Breakdown
Investing Cost Breakdown
Land and Site Cost, Equipment Cost, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Contingency, Engineering and Consulting Charges

Enterprise Plan
USD 4,799
USD 4,079
Includes all Report Content
Key Processing Information, Capital Investment Analysis, Conversion Cost Analysis, Variable Cost Breakdown, Investing Cost Breakdown,
Equipment Cost Breakdown
Breakdown of Machinery Cost By Equipment, Auxiliary Equipment Cost, Piping, Electrical, Instrumentation
Land and Construction Cost Details
Land Cost, Development Charges, Cost of Construction, Plant Building, Site Development Charges
Dynamic Excel Cost Model
Dynamic Spreadsheet (Unlocked)
*Please note that the prices mentioned below are starting prices for each bundle type. Kindly contact our team for further details.*
Flash Bundle
Number of Reports: 3
20%
tax inclusive*
Small Business Bundle
Number of Reports: 5
25%
tax inclusive*
Growth Bundle
Number of Reports: 8
30%
tax inclusive*
Enterprise Bundle
Number of Reports: 10
35%
tax inclusive*
How To Order
Our step-by-step guide will help you select, purchase, and access your reports swiftly, ensuring you get the information that drives your decisions, right when you need it.

Select License Type
Choose the right license for your needs and access rights.

Click on ‘Buy Now’
Add the report to your cart with one click and proceed to register.

Select Mode of Payment
Choose a payment option for a secure checkout. You will be redirected accordingly.
Gain insights to stay ahead and seize opportunities.
Get insights & trends for a competitive edge.
Track prices with detailed trend reports.
Analyse trade data for supply chain insights.

Leverage cost reports for smart savings
Enhance supply chain with partnerships.

Connect For More Information
Our expert team of analysts will offer full support and resolve any queries regarding the report, before and after the purchase.
Our expert team of analysts will offer full support and resolve any queries regarding the report, before and after the purchase.
We employ meticulous research methods, blending advanced analytics and expert insights to deliver accurate, actionable industry intelligence, staying ahead of competitors.
Our skilled analysts offer unparalleled competitive advantage with detailed insights on current and emerging markets, ensuring your strategic edge.
We offer an in-depth yet simplified presentation of industry insights and analysis to meet your specific requirements effectively.


Australia
63 Fiona Drive, Tamworth, NSW
+61-448-061-727
India
C130 Sector 2 Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301
+91-723-689-1189
Philippines
40th Floor, PBCom Tower, 6795 Ayala Avenue Cor V.A Rufino St. Makati City,1226.
+63-287-899-028, +63-967-048-3306
United Kingdom
6 Gardner Place, Becketts Close, Feltham TW14 0BX, Greater London
+44-753-713-2163
United States
30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801
+1-415-325-5166
Vietnam
193/26/4 St.no.6, Ward Binh Hung Hoa, Binh Tan District, Ho Chi Minh City
+84-865-399-124
United States (Head Office)
30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801
+1-415-325-5166
Australia
63 Fiona Drive, Tamworth, NSW
+61-448-061-727
India
C130 Sector 2 Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301
+91-723-689-1189
Philippines
40th Floor, PBCom Tower, 6795 Ayala Avenue Cor V.A Rufino St. Makati City, 1226.
+63-287-899-028, +63-967-048-3306
United Kingdom
6 Gardner Place, Becketts Close, Feltham TW14 0BX, Greater London
+44-753-713-2163
Vietnam
193/26/4 St.no.6, Ward Binh Hung Hoa, Binh Tan District, Ho Chi Minh City
+84-865-399-124
Share